Numerical Treatment of Nonlinear Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equation with a Generalized Singular Ker
Vol.06No.03(2016), Article ID:70594,6 pages
10.4236/ajcm.2016.63025
Fatheah Ahmed Hendi1, Manal Mohamed Al-Qarni2
1Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science, King Abdul Aziz University, Jeddah, KSA
2Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science, King Khaled University, Abha, KSA

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 11 July 2016; accepted 11 September 2016; published 14 September 2016
ABSTRACT
In the paper, the approximate solution for the two-dimensional linear and nonlinear Volterra- Fredholm integral equation (V-FIE) with singular kernel by utilizing the combined Laplace-Ado- mian decomposition method (LADM) was studied. This technique is a convergent series from easily computable components. Four examples are exhibited, when the kernel takes Carleman and logarithmic forms. Numerical results uncover that the method is efficient and high accurate.
Keywords:
Singular Integral Equation, Linear and Nonlinear V-FIE, Adomian Decomposition Method (ADM), Carleman Kernel, Logarithmic Kernel

1. Introduction
The V-FIE arises from parabolic boundary value problems. In practical applications one frequently encounters the V-FIE with singular kernel of the form
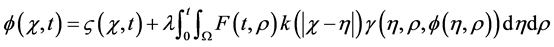 (1)
(1)
The functions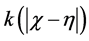 ,
, 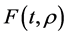 and
and 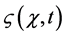 are given and called the kernel of Fredholm integral term, Volterra integral term and the free term respectively and
are given and called the kernel of Fredholm integral term, Volterra integral term and the free term respectively and 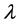 is a real parameter (may be complex and has physical meaning). Also, Ω is the domain of integration with respect to position, and the time t,
is a real parameter (may be complex and has physical meaning). Also, Ω is the domain of integration with respect to position, and the time t,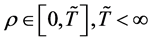 . While
. While 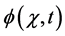 is the unknown function to be determined in the space
is the unknown function to be determined in the space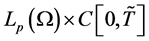 . In [1] Abdou et al. studied the existence and uniqueness of solution of V-FIE.
. In [1] Abdou et al. studied the existence and uniqueness of solution of V-FIE.
There are several techniques that have been utilized to handle the integral Equation (1), in [2] - [5] a few techniques, for example, the projection method, time collocation method, the trapezoidal Nystrom method, and furthermore analytical or numerical techniques were utilized to treated this equation, but this techniques experienced troubles as far as computational work utilized. In [6] treated Maleknejad and Hadizadeh Equation (1) by using the ADM presented in [7] - [9] .
Many authors have studied solutions of two-dimensional linear and nonlinear integral equations by utilizing different techniques, such as Abdou et al. in [10] discussed the solution of linear and nonlinear Hammerstien integral equations with continuous kernel and used two different methods (Adomian decomposition method and homotopy analysis method). Abdou et al. in [11] - [13] considered the integral equation with singular kernel and used Toeplitz matrix and product Nystrom methods to obtain the solution. In [14] El-Kalla and Al-Bugami used ADM and degenerate kernel method for solving nonlinear V-FIE with continuous kernel.
In this paper, we will discuss the combined (LADM) to approximate solutions with high degree of accuracy for V-FIE with a generalized singular kernel.
2. The Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving V-FIE
Consider the integral equation
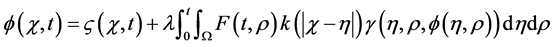 (2)
(2)
The (ADM) introduces the following expression
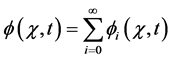 (3)
(3)
for the solution 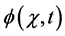 of Equation (2), where the components
of Equation (2), where the components  will be determined recurrently. Moreover, the method defines the nonlinear function
will be determined recurrently. Moreover, the method defines the nonlinear function 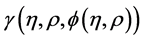 by an infinite series of polynomials
by an infinite series of polynomials
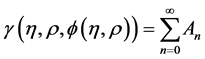 (4)
(4)
where 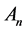 are the so-called Adomian polynomials that represent the nonlinear term
are the so-called Adomian polynomials that represent the nonlinear term  and can be calculated for various classes of nonlinear operators according to specific algorithms set by Adomian [8] [9] . A new algorithm for calculating these polynomials was established by Wazwaz [15] [16] .
and can be calculated for various classes of nonlinear operators according to specific algorithms set by Adomian [8] [9] . A new algorithm for calculating these polynomials was established by Wazwaz [15] [16] .
Substituting Equation (3) and Equation (4) into Equation (2) yields
 (5)
(5)
The components  are computed using the following recursive relations
are computed using the following recursive relations
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
Relations (6,7) will enable us to determine the components  recurrently, and as a result, the series solution of
recurrently, and as a result, the series solution of  is readily obtained.
is readily obtained.
3. Laplace Adomian Decomposition Method Applied to V-FlE with Singular Kernel
3.1. Carleman Kernel
We assume that the kernel  of Equation (1) takes the form
of Equation (1) takes the form , [17] then integral Equation (1) can be expressed as:
, [17] then integral Equation (1) can be expressed as:
 (8)
(8)
Applying the Laplace transform to both sides of Equation (8) gives:
 (9)
(9)
The ADM can be used to handle Equation (9). We represent the linear term  from Equation (3) and the nonlinear term
from Equation (3) and the nonlinear term  will be represented by the Adomian polynomials from Equation (4).
will be represented by the Adomian polynomials from Equation (4).
Substituting Equation (3) and Equation (4) into Equation (9) leads to
 (10)
(10)
The ADM introduces the recursive relation

 (11)
(11)
Applying the inverse Laplace transform to the first part of Equation (11) gives . Utilizing
. Utilizing  will empower us to evaluate
will empower us to evaluate , and so on. This will prompt the complete determination of the components of
, and so on. This will prompt the complete determination of the components of  upon utilizing the second part of Equation (11). The series solution follows promptly after utilizing Equation (3). The obtained series solution may converge to an exact solution if such a solution exists.
upon utilizing the second part of Equation (11). The series solution follows promptly after utilizing Equation (3). The obtained series solution may converge to an exact solution if such a solution exists.
3.2. Logarithmic Kernel
We assume that the kernel  of Equation (1) takes the form
of Equation (1) takes the form , [17] then integral Equation (1) can be expressed as:
, [17] then integral Equation (1) can be expressed as:
 (12)
(12)
Applying the Laplace transform to both sides of Equation (12) gives:
 (13)
(13)
Using the same method we shall find at the end the required solution by the inverse of Laplace transform.
4. Numerical Examples
4.1. Application for Carleman Kernel and Logarithmic Kernel
We consider two examples for the integral equation
 (14)
(14)
 , the exact solution
, the exact solution 
We consider the linear and nonlinear cases: respectively, for the Carleman kernel
respectively, for the Carleman kernel
 and the computing results are obtained when
and the computing results are obtained when  where
where  is called Poisson’s coefficient,
is called Poisson’s coefficient,  , while the kernel in the second example takes the logarithmic kernel
, while the kernel in the second example takes the logarithmic kernel  and the results are computing, using Maple 17 at
and the results are computing, using Maple 17 at  and
and .
.
Example 1 [(see 1)]: Consider the V-FIE with Carleman kernel
 (15)
(15)
 , the exact solution
, the exact solution 
Using Maple 17, we obtain Table 1 and Table 2
Example 2 [(see 1)]: Consider the V-FIE with logarithmic kernel
 (16)
(16)
 , the exact solution
, the exact solution 
Using Maple 17, we obtain Table 3 and Table 4
Table 1. Results obtained for example 1 and error (Linear case, ).
).
Table 2. Results obtained for example 1 and error (Nonlinear case, ).
).
Table 3. Results obtained for example 2 and error (Linear case, ).
).
4.2. Application for a Generalized Carleman Kernel and Logarithmic Kernel
Example 3 [(see 11, 13)]: Consider the V-FIE with generalized Carleman kernel
 (17)
(17)
 , the exact solution
, the exact solution 
Using Maple 17, we obtain Table 5.
Example 4 [(see 11,13)]: Consider the V-FIE with generalized logarithmic kernel
 (18)
(18)
 , the exact solution
, the exact solution ,
,
Using Maple 17, we obtain Table 6.
Table 4. Results obtained for example 2 and error (Nonlinear case, ).
).
Table 5. Results obtained for example 3 and error.
Table 6. Results obtained for example 4 and error.
5. Conclusion
In this study, we considered linear and nonlinear integral equations of type Volterra-Fredholm with singular kernel. We have proven that the (LADM) is effective and useful technique for solving these kinds of integral equations with singular kernel and many nonlinear problems, efficiency and accuracy of the introduced method are illustrated by four numerical examples which showed simplicity of this method.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the King Abdulaziz city for science and technology.
Cite this paper
Fatheah Ahmed Hendi,Manal Mohamed Al-Qarni, (2016) Numerical Treatment of Nonlinear Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equation with a Generalized Singular Kernel. American Journal of Computational Mathematics,06,245-250. doi: 10.4236/ajcm.2016.63025
References
- 1. Abdou, M.A., Hendi, F.A. and Abu Alnaja, K.J.M. (2012) Toeplitz Matrix Method and Volterra-Hammerstin Integral Equation. Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics, 70, 103-121.
- 2. Hacia, L. (1996) On Approximate Solution for Integral Equations of Mixed Type. ZAMM. Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 76, 415-416.
- 3. Kauthen, P.J. (1989) Continuous Time Collocation Methods for Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equations. Numerische Mathematik, 56, 409-424.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01396646 - 4. Han, G.Q. and Zhang, L.Q. (1994) Asymptotic Expansion for the Trapezoidal Nystrom Method of Linear Volterra-Fredholm Equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 51, 339-348.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0377-0427(92)00013-Y - 5. Brunner, H. (1990) On the Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equation by Collocation Methods. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 27, 987-1000.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/0727057 - 6. Maleknejad, K. and Hadizadeh, M. (1999) A New Computational Method for Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equations. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 37, 1-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0898-1221(99)00107-8 - 7. Cherruault, Y., Saccomandi, G. and Some, B. (1992) New Results for Convergence of Adomian’s Method Applied to Integral Equations. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 16, 85-93.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0895-7177(92)90009-A - 8. Adomian, G. (1991) A Review of the Decomposition Method and Some Recent Results for Nonlinear Equation. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 21, 101-127.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0898-1221(91)90220-X - 9. Adomian, G. (1994) Solving Frontier Problems of Physics: The Decomposition Method. Kluwer.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8289-6 - 10. Abdou, M.A., El-Kalla, I.L. and Al-Bugami A.M. (2011) New Approach for Convergence of the Series Solution to a Class of Hammerstein Integral Equations. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation, 3, 261-269.
- 11. Abdou, M.A., El-Kalla, I.L. and Al-Bugami A.M. (2011) Numerical Solution for Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equation with A Generalized Singular Kernel. Journal of Modern Methods in Numerical Mathematics, 2, 1-15.
http://dx.doi.org/10.20454/jmmnm.2011.60 - 12. El-Kalla, I.L. and Al-Bugami A.M. (2011) Fredholm-Volterra Integral Equation with A Generalized Singular Kernel and Its Numerical Solutions. IJRRAS, 6, 341-352.
- 13. Al-Bugami, A.M. (2013) Toeplitz Matrix Method and Volterra-Hammerstin Integral Equation with a Generalized Singular Kernel. Progress in Applied Mathematics, 6, 16-42.
- 14. El-Kalla, I.L. and Al-Bugami A.M. (2012) Numerical Solution for Nonlinear Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equation with Applications in Torsion Problems. International Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 7, 403-418.
- 15. Wazwaz, A.M. (2002) A Reliable Treatment for Mixed Volterra-Fredholm Integral Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 127, 405-414.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(01)00020-0 - 16. Wazwaz, A.M. (2000) A New Algorithm for Calaculating Adomian Polynomials for Nonlinear Operators. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 111, 53-59.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(99)00063-6 - 17. Hendi, F.A. (2011) Laplace Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving the Nonlinear Volterra Integral Equation with Weakly Kernels. Studies in Nonlinear Sciences, 2, 129-134.
上一篇:On the Location of Zeros of Po 下一篇:Some Properties of the g-Good-
最新文章NEWS
- Auto-Bäcklund Transformation and Extended Tanh-Function Methods to Solve the Time-Dependent Coeffici
- A Third-Order Scheme for Numerical Fluxes to Guarantee Non-Negative Coefficients for Advection-Diffu
- Conjugate Effects of Radiation and Joule Heating on Magnetohydrodynamic Free Convection Flow along a
- An O(k<sup>2</sup>+kh<sup>2</sup>+h<sup>2</sup>) Accurate Two-le
- On the Location of Zeros of Polynomials
- Peristaltic Pumping of a Conducting Sisko Fluid through Porous Medium with Heat and Mass Transfer
- An Accurate Numerical Integrator for the Solution of Black Scholes Financial Model Equation
- Simulation of Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation in the Position and Momentum Domains
推荐期刊Tui Jian
- Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine
- Journal of Genetics and Genomics
- Journal of Bionic Engineering
- Pedosphere
- Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry
- Nuclear Science and Techniques
- 《传媒》
- 《中学生报》教研周刊
热点文章HOT
- Asymptotic Solutions for the Fifth Order Critically Damped Nonlinear Systems in the Case for Small E
- Partial Fraction Decomposition by Repeated Synthetic Division
- Higher-Order Numerical Solution of Two-Dimensional Coupled Burgers’ Equations
- Group Method Analysis of MHD Mixed Convective Flow Past on a Moving Curved Surface with Suction
- Simple and Multi Linear Regression Model of Verbs in Quran
- Conjugate Effects of Radiation and Joule Heating on Magnetohydrodynamic Free Convection Flow along a
- Peristaltic Pumping of a Conducting Sisko Fluid through Porous Medium with Heat and Mass Transfer
- An O(k<sup>2</sup>+kh<sup>2</sup>+h<sup>2</sup>) Accurate Two-le

